Investing in property renovations is a crucial strategy for increasing property value and maximizing return on investment (ROI). To determine the best renovation strategy, we need to evaluate various renovation options and their potential impacts on property value. Using Branch and Bound algorithm, we can break down this complex decision-making process into manageable steps, ensuring we make the most informed investment decisions. This approach allows us to consider multiple factors and choose the renovation strategy that yields the highest ROI, despite varying market conditions.
Branch and Bound Algorithm
Branch and Bound algorithm is a method used to solve optimization problems. It systematically explores and prunes branches of a decision tree, where each branch represents a potential solution. By calculating an upper bound for each branch, it eliminates branches that cannot produce a better solution than the current best one, thus efficiently finding the optimal solution.
Implementation
Each renovation option has:
- A cost
- A potential value increase
- We can add more feilds into here.
The constraints are:
- The total cost of selected renovation options should not exceed the given budget.
- Can add more constraints like bathrooms must be compulsary renovated.
Objective: Maximize the total value increase from the selected renovation options.
Steps
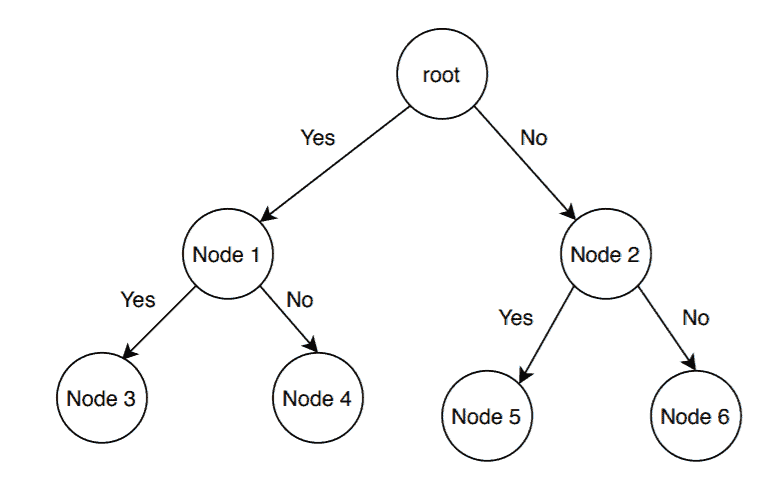
1. Create a State Space Tree
- Nodes: Each node represents a decision to include or exclude a renovation option.
- Branching: For each node, there are two possible branches:
- Include the renovation option.
- Exclude the renovation option.
2. Calculate Upper Bound
- Upper Bound Calculation: For each node in the tree, calculate an upper bound of the maximum possible value that can be obtained from that node. This helps in estimating the potential value of the node and deciding whether to continue exploring that branch.
3. Removing Branches
- Excluding branch Criteria: If the upper bound of a node is less than the current best value found, discard that branch. This avoids exploring branches that cannot yield a better solution than the best one found so far.
4. Track the Best Solution
- Tracking: Keep track of the best solution found during the exploration of the state space tree.
Time and Space Complexity.
- Time Complexity:
O(b*d)b: branching factor d:depth - Space Complexity:
O(b*d)
 Optimizing Property Connections with Essentials Around the area
Optimizing Property Connections with Essentials Around the area 